Working With C
Dan Goldsmith
Introduction
Introduction
- Look at C and C++
- Look at compilation process
- Representing of code on Micro controller
Program Language Styles
In the Beginning, there was assembly.
; linker puts the entry point here:
_start:
; Write the string to stdout:
mov edx,len ;message length
mov ecx,msg ;message to write
mov ebx,1 ;file descriptor (stdout)
mov eax,4 ;system call number (sys_write)
int 0x80 ;call kernel
; Exit via the kernel:
mov ebx,0 ;process' exit code
mov eax,1 ;system call number (sys_exit)
int 0x80 ;call kernel - this interrupt won't return
Amazing Grace

The Invention of High Level Languages
- Admiral Grace Hopper.
- Invented the Compiler and COBOL
It’s much easier for most people to write an English statement than it is to use symbols. So I decided data processors ought to be able to write their programs in English, and the computers would translate them into machine code.
Monolithic Programming
- Code in one huge block
- Use of GOTO statements
Monolithic
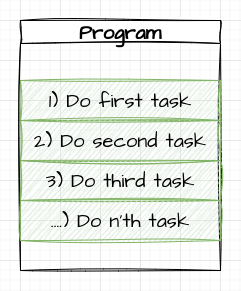
C (Procedural)
- C has a procedural view of programming
- Focus on the Functions we have to perform
- Improvement as we break code into reusable, logical, chunks
C
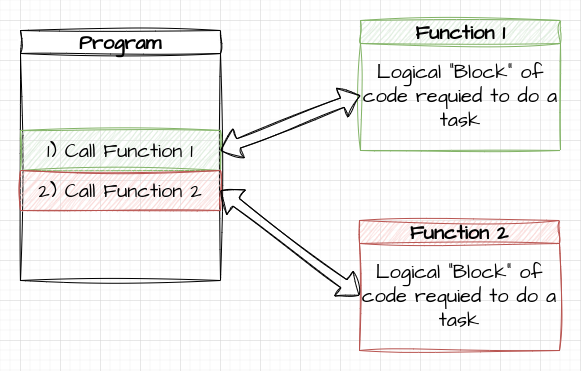
C++ (Object Orientated)
- C++ Introduced classes
- Object orientated
- Focus on both the functions and the data associated with them.
C++
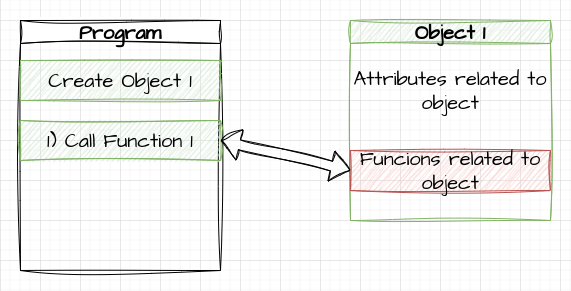
C and C++
- The basics are similar
- Pre-defined, strongly typed variables
- Syntax is very similar
In MBED OS
- Differences are less pronounced
- “C with Classes”
- No desktop style stdlib
- use mbed.h
C Programming Language overview
Learning C
- Can be a bit intimidating depending on background
- Typing, Pointers etc unfamiliar to Python users
- Secret is to:
- Think like a programmer
- Practice
Thinking like a programmer
- We shouldn’t learn Python / C / Java
- Instead basic building blocks of a program
- Syntax is just “magic words” to achieve this.
- (Yes there are language specific quirks)
What Makes a Program
- Importing Libraries
- Defining and using Variables
- Selection and Iteration
- Classes and Function Calls
What makes a program
- Think about the Logical flow of what we want to do
- How do we represent that in our building blocks
- Implement in language specifics
Practice
I hear and I forget. I see and I remember. I do and I understand.
Confucius
C Program Components
- Preamble: Import libraries, setup global
- Main(): Entry Point to the program
Hello world.
#include
int main() {
// put your setup code here, to run once:
//Setup the LED1 pin to be a digital output called ledOne
DigitalOut ledOne(LED1);
while(1) {
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
printf("Loop\n");
ledOne = 1;
ThisThread::sleep_for(500ms);
ledOne = 0;
ThisThread::sleep_for(500ms);
}
}
Preamble
- Used to import relevant libraries
- Used to set global variables.
Program Code
- Can be broken into different functions
- main() is our entry point
- tells the program where to start.
Program Code
Compiled Code
- C is a compiled language
- Start with high level “human readable” representation
- Use a compiler to turn this into machine level representation
Code Compile Process
- Lexing: Break high level code into a set of tokens
- Parsing: Derive meaning from tokens, and build AST
- Intermediate Stage Use AST to generate intermediate code (for example ASM)
- Compile Turn AST into machine level language.
C: General Syntax
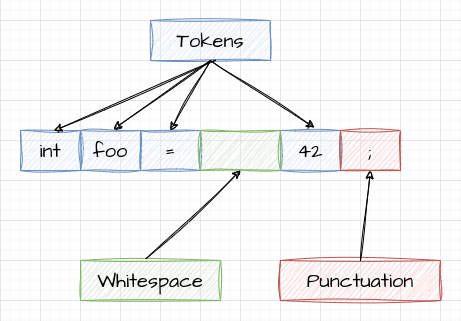
C: Tokens
Tokens: Identifiers
- A name we have defined for something
- Variables / Constants
- Case Sensitive
Tokens: Identifiers
int led;- led is the identifier
char* thestring[50];- thestring is the identifier
Tokens: Literals
- A data value expressed directly in the code
int led=5;- Set the value of led to 5
string name="dan";- Set the value of name to dan
char letter=0x42;- Set the value of letter to 0x42 (hex representation)
Tokens: Operators
- A symbol representing an operation to be performed.
- arithmetic, logical, assignment etc.
int a = 5+1- = is assignment
- + addition
1==1- == Check for equality.
Tokens: Keywords
- Have special meaning in the language
- Declaring Variable Types
- Iteration and Selection
- Cannot be used as Identifiers
Tokens: Keywords
int foo- Declare foo to be of type int
while (1)- Next block of code is a while loop
if (foo == 1)- Selection operator
White space
- Not “Important” to C (unlike python)
- Still important for readability
- White space (IE Indentation) is a good idea
- See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/International_Obfuscated_C_Code_Contest
White space
int x=5; while (x > 0){ printf("Value of X is %d\n", x); }White space
int x=5;
while (x > 0){
printf("Value of X is %d\n", x);
}Punctuation
- Used to represent sets of instructions
- Statements end in
; - Blocks enclosed in
{ }
- Statements end in
Punctuation
- Common cause of problems
- Especially when switching from Python etc.
- Compiler will do its best to help us with error messages.
src/main.cpp: In function 'int main()':
src/main.cpp:14:5: error: expected ';' before 'ledOne'
ledOne = 1;C common tasks
Common Tasks
- How do we do common programming tasks in C:
- Defining Variables
- Selection and Iteration
Defining Variables
- C is strongly typed
- Means we need to tell compiler what our variable is expected to be
- Contrast with weakly typed python
Defining Variables
- Behind the Scenes
- Part of function preamble, and process control
- Space is pre-allocated on the stack for each variable
Variable Size
- Can be an issue in embedded development
- Different target boards may have different widths
- Should be OK if we use a specific chipset (ie STM32)
Variable Size
- Byte 8 Bits
- Half Word 16 Bits
- word 32 Bits
- dword 64 Bits
C: Variable Types
- int Integer (whole) numbers
- float Floating point (decimal) numbers
- char Single Characters
- char* Character Array
C: Variable Types

Selection
- Used when we have a choice to make.
if (variable == value){
//do something
}
else{
//Do something else
}Iteration
- Used when we want to repeat ourselves.
- Two main types
- for if we know the number of times we will repeat
- while keep going until a condition is met.
Iteration: For Loops
for (int x=0; x<10; x++){
//do something
}Iteration: While Loops
int x=0 //Start condition
while (x<10){
//do something
x+=1 // DON'T forget to update the condition
}Functions: Allow us to break code into Logical blocks
int add(int first, int second){
int out = first+second;
return out;
}Classes
class flasher {
//variables go here
//Methods go here
int add(int first, int second){
...
}
}Q&A Time
- Questions?